Medical billing keeps healthcare running, but mistakes are common; roughly 80% of bills have errors, costing the system nearly $125 billion and delaying payments for months. That’s where EMR in Medical Billing comes in: electronic medical records centralize clinical data, add validation checks, and automate parts of coding and claims submission.
Moreover, in this article, we’ll explain what EMR in medical billing is, how it reduces denials and delays, and why it’s becoming essential for modern practices.
What is EMR in Healthcare?
An electronic medical record system (EMR) is a digital version of a patient’s paper chart. It includes medical history, diagnoses, treatments, prescriptions, and other details recorded by doctors.
In medical billing, EMRs connect clinical information with billing systems. This helps healthcare providers code services correctly, prove that treatments were necessary, and send clean, error-free claims to insurance companies.
Unlike older digital records that often store scanned files, electronic medical record systems are organized, searchable, and easy to share within a practice. This makes it faster to find information and link it with billing codes.
- It’s also helpful to know the difference between EMRs and EHRs (Electronic Health Records).
- Medical EMR systems are primarily used in a single clinic or hospital to manage patient records and billing.
- EHRs allow patient information to be shared across different healthcare organizations for more complete care.
How EMR Improves Medical Billing
Medical billing errors often occur when patient information is scattered across paper files or outdated systems. Electronic Medical Records (EMR) solve this by centralizing data and directly connecting it with billing workflows.
Instead of manually re-entering details, providers can pull accurate codes, insurance data, and treatment notes straight from the electronic medical record system. This integration ensures billing is precise, efficient, and up to date.
Here’s how EMRs improve medical billing:
- Cuts billing errors by up to 80% through automation.
- Speeds up claim approvals by 25%, helping providers get paid faster.
- Reduces denials by nearly 40% when EMRs are integrated with billing systems.
- Prevents 90% of common claim issues with accurate, real-time coding.
- Boosts revenue by up to 15% while lowering admin costs by 18%.
By automating claim preparation and reducing manual work, medical EMR systems make billing smoother, minimize denials, and save staff valuable time. The result is higher accuracy, faster payments, and improved compliance, benefiting both healthcare providers and patients.
Benefits of EMR in Medical Billing
1. More Accurate Billing
EMRs make billing more reliable by clearly recording patient details and automatically suggesting the correct medical codes. This reduces errors that often cause claim denials.
2. Faster Insurance Claims
With EMRs linked directly to billing software, claims can be submitted electronically within minutes. This faster process improves cash flow and ensures providers get paid quickly.
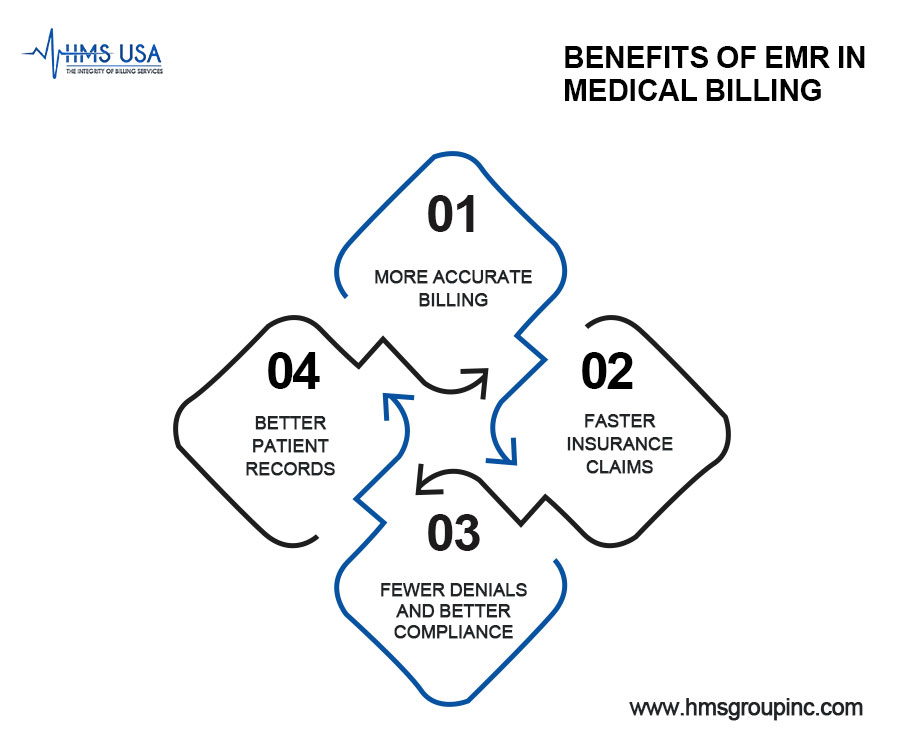
3. Fewer Denials and Better Compliance
Built-in compliance checks in EMRs help providers meet insurance and regulatory requirements. This reduces costly denials and keeps practices audit-ready.
4. Better Patient Records
Since EMRs centralize medical and billing information, providers get a complete view of a patient’s history. This not only supports accurate billing but also improves overall care coordination.
EHR vs EMR: What’s the Difference
Although the terms are often used interchangeably, EMRs and EHRs are not the same.
- EMR (Electronic Medical Records): Works like a digital version of a paper chart for one practice. It stores patient history, diagnoses, and treatments, making it valid for billing within a single clinic or hospital.
- EHR (Electronic Health Records): Goes beyond one practice. It’s designed to be shared across hospitals, specialists, and labs, giving a broader picture of patient care.
HMS USA INC offers professional medical billing services that expedite claim approvals and reduce denials.
List of EMR Systems in Healthcare
Healthcare providers can choose from different types of EMR systems, depending on their size, budget, and specialty.
On-Premises EMRs
Installed directly at the facility, these give complete control over data and allow deep customization. However, they involve high upfront costs, ongoing maintenance, and dedicated IT support, making them more common in large hospitals than in small clinics.
Cloud-Based EMRs
Accessible from anywhere with an internet connection, these are more affordable and easier to update. They don’t require heavy hardware, which makes them ideal for small to medium-sized practices looking for flexible, budget-friendly solutions.
Specialty-Specific EMRs
Built for fields like paediatrics, behavioral health, or dental care, digital medical records systems include pre-made templates tailored to each specialty. This not only simplifies documentation but also improves coding accuracy and billing efficiency for niche practices.
Uses of EMR Beyond Billing
While medical EMR systems are a potent tool for billing, their benefits extend much further in healthcare:
Helping Doctors Make Better Decisions: By keeping all patient information in one place, EMRs can flag drug interactions and even suggest treatment options.
Improving Teamwork in Care: EMRs let doctors, nurses, and specialists share records instantly. This avoids duplicate tests and ensures coordinated care.
Tracking Health Over Time: From monitoring chronic conditions to evaluating treatment progress, EMRs make long-term care more effective.
Why EMRs Matter in Today’s Healthcare
Electronic Medical Records play a vital role in modern healthcare by linking patient care with financial processes. By integrating with billing systems, EMRs reduce costly errors, improve compliance, and ensure providers are reimbursed accurately for the care they deliver.
Beyond billing, EMRs support the industry’s shift toward value-based care by tracking outcomes, measuring provider performance, and enabling payment models that reward quality instead of quantity.
Looking ahead, innovations like artificial intelligence and automation will make digital medical records even smarter, from predicting health risks early to simplifying documentation and boosting patient engagement.
Final Words
EMR in medical billing is more than digital charts; it connects patient care, billing, and compliance in one streamlined system. By reducing errors, automating claim submissions, and improving patient outcomes, EMRs make healthcare practices more efficient and financially stable.
When clinics and hospitals choose the right digital medical records system, they not only improve care but also strengthen their medical billing process, ensuring timely reimbursements and fewer denials.
If you want to make your billing and patient care more efficient with the help of EMRs, contact HMS Group Inc. today to see how we can support your practice.
FAQs
What is EMR in medical billing?
An EMR (Electronic Medical Record) is a digital version of a patient’s chart. In billing, it helps record visits, track treatments, and generate accurate claims for insurance companies.
How is EMR different from EHR?
EMRs are usually limited to one practice, storing records for a single provider or clinic. EHRs (Electronic Health Records) are broader, allowing information sharing across multiple providers, hospitals, or specialists.
What are the types of EMR systems?
- On-Premises EMR – installed at the clinic, offering control but requiring high maintenance.
- Cloud-Based EMR – stored online, affordable, and accessible anywhere.
- Speciality-Specific EMR – built for unique fields like paediatrics, dental, or behavioral health.
What are the benefits of using EMR in billing?
EMRs reduce coding errors, speed up insurance approvals, cut down on claim denials, and keep records organized for accurate billing and compliance.
Can EMR systems help with patient care, too?
Yes. EMRs support better decision-making by storing complete medical histories, alerting providers to drug interactions, and making care coordination easier across teams.