
Simplifying The Health Insurance Billing Process
Understanding health insurance billing is crucial for both; individuals seeking medical care and healthcare professionals providing services. Navigating the complexities of the insurance billing process can be daunting. However, with a solid grasp of the basics, healthcare practices can streamline their billing process and ensure timely reimbursement.
This blog post will shed light on the basics of insurance billing and delve into how insurance billing works and the intricacies of health insurance billing.
Health Insurance Billing Basics Explained
The health insurance billing process is an integral part of the healthcare system. It plays a vital role in ensuring that the patient receives quality care while the healthcare provider gets payments timely for the services they provide. But what exactly does the health billing process entail?
Health insurance billing refers to the systemic process of submitting claims to insurance companies and following up on them. This ensures timely reimbursement for the services rendered to patients. It involves translating medical diagnosis, treatment, and procedures into alphanumeric standard codes. Such as CPT (Current Procedural Terminology) codes and ICD (International Classification of Diseases) codes which are used to describe and classify healthcare services.
Healthcare providers which include physicians, hospitals, and clinics, submit claims to the insurance companies on behalf of their patients. These claims will review by the insurance service provider and then processed. After the claim get approves, health insurance companies issue payment to the healthcare provider or the third-party billing company. However, in case a claim is denied, the provider or billing expert needs to identify errors in the billing process and rectify them before submitting the claim again.
The process of health insurance billing involves a lot of paperwork. Furthermore, various regulations make it a complex process that requires specialized expertise.
Overall, healthcare insurance billing plays a crucial role in ensuring that healthcare providers are compensated accurately for the services they deliver. Thus, enabling them to continue providing quality care to patients along with maintaining the financial stability of their practice. Read more
How Does Insurance Billing Work?
The health insurance billing process may seem like an overly complicated process that is too hard to grasp. So here is a simplified version, explaining the billing process by breaking it down into 8 basic steps that are essential for insurance billing:
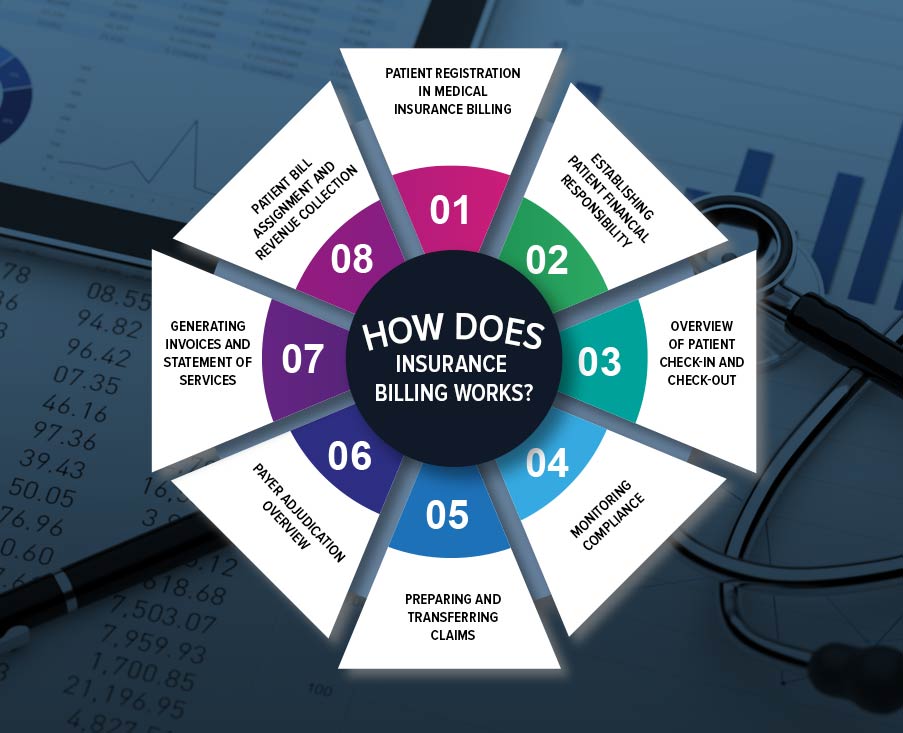
Patient Registration in Medical Insurance Billing
Patient registration is the initial step in the medical insurance billing process. This process will initiate when the patient contacts the healthcare practice to schedule an appointment. For new patients, demographic details, including their name, date of birth, contact number, the reason for visit, and insurance details keep the record. Details related to insurance include the name of the insurance provider, type of insurance policy, and patient’s policy number. Healthcare practices or third-party billing companies then make a dedicated file for this patient. However, if the patient is a regular visitor of the practice, then this step will not be repeated with each appointment.
Establishing Patient Financial Responsibility
Each insurance company has its own set of regulations for insurance coverage and reimbursement following medical claim processing. It is necessary to confirm or establish financial liability for the patient to ensure the service is covered under the insurance policy. The process enables the patient to have an understanding of what services are managed by their insurance company and what expenses they are responsible for after the insurance portion is applied. By knowing this information, patients can make informed decisions about whether to utilize the service or not.
Overview of Patient Check-in and Check-out
Patient check-in and check-out procedures are relatively uncomplicated and can be handle effectively. Upon arriving at a healthcare facility, patients are typically requires to fill out necessary forms pertaining to their purpose of visit. New patients have to fill out some additional forms.
During the check-out process, the medical biller or coder carefully extracts all the relevant information from the documents. It includes the medical history and treatment provided. It is then translated into accurate medical codes thus creating a document that is referred to as ‘superbill’. The superbill serves as essential information for generating claims. Once complete, the superbill is transferred typically through a software program to medical billers.
Monitoring Compliance
In the healthcare insurance billing process, compliance with the Office of the Inspector General (OIG) and the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) is strictly adhered to. After inputting necessary information into the software, the biller performs additional checks. This is to ensure compliance standards are met. Moreover, this meticulous review ensures that the insurance billing process is accurately and appropriately crafted following all relevant guidelines and regulations.
Preparing and Transferring Claims
In accordance with the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act of 1996 (HIPAA), claims and transactions in healthcare insurance billing are transferred electronically for efficient processing. Manual claims are still acceptable, however, they are prone to errors. Moreover, they have low levels of efficiency which takes longer to get reimbursement.
Healthcare practices often seek help from third-party medical billing service providers to streamline health insurance billing. These service providers help with accurate claim submission. It thus reduces the workload and ensures efficient handling of the billing cycle.
Payer Adjudication Overview
Payer adjudication is an integral step in the billing process. In this process, the healthcare payer, that is the insurance company, evaluates claims, codes, compliance, and charges to determine whether to accept them. The evaluation follows predefined guidelines. For healthcare facilities to receive reimbursements, they must submit clean claims to insurance service providers.
Coding errors, often made by billers and coders are the most common reason for claim denials. This is due to frequent changes in regulations by CMS, affecting healthcare practices and insurance service providers. Moreover, insurance payers often have policies that the patients and healthcare providers have to adhere to.
Generating Invoices and Statement of Services
Once the claim gets approved, the biller, or third-party company, receives a report detailing the services that have been paid by the insurance company. The biller then communicates to the patient about the payment that were due upon by the insurance service provider. If there is any remaining amount then it is paid by the patient. This process involves creating invoices and statements that clearly outline. The services provided, the payments made by the insurance service provider, and the patient’s financial responsibility.
Patient Bill Assignment and Revenue Collection
The final step in the process of insurance billing involves the collection of payments for services provided by patients. Medical billers are responsible for sending bills to patients and monitoring outstanding payments if any. In settings where payments are delayed or not made, billers are given the task to follow up and remind patients through various channels. This includes emails, text messages, and phone calls. The billers play a crucial role in ensuring timely bill payments.
Additionally, healthcare providers can seek assistance from professional billing agencies to help streamline the collection of payments from patients. These agencies specialize in managing payment collections and can provide support to healthcare providers in the revenue collection process.
Conclusion
The healthcare insurance billing cycle is undoubtedly complex and prone to errors. By understanding insurance billing basics, comprehending how it works, and recognizing the intricacies of the billing process, healthcare practices can navigate the system more effectively. It can aid healthcare providers to thrive in the industry by optimizing the revenue of the practice along with providing quality patient care.
FAQ's
Payment posting in health insurance billing involves recording and documenting payments received from insurance companies into billing software.
Claim is referred to as a clean claim when it is accurate and filled out, with all required information and supporting documentation provided. Clean claims have a higher chance exception and process promptly by insurance companies.
The CPT code for diagnostic mammography when performed unilaterally is 77065. Whereas, when the mammography is performed bilaterally, the CPT code is 77066.
The CPT code for a flexible colonoscopy procedure with control of bleeding through any method is 45382. Whereas, the CPT codes for flexible colonoscopy for the removal of polyps, tumors, or other lesions by hot biopsy method and snare technique are 45384 and 45385 respectively.
The CPT code 322758 use to bill metabolic panel lab tests.








