
Everything You Need to Know About Hospital Provider Credentialing Process
Whether you work in a busy hospital or private practice, hospital credentialing process is about giving patients peace of mind. Examining a provider’s qualifications, training, licenses, experience, and professional background is essential for hospital credentialing. Are you ready to learn hospital credentialing secrets? Let’s explore this crucial adventure.
Understanding Hospital Credentialing Process
Physician credentialing for hospitals quality standards were developed by the Joint Commission in 1951. Since its founding, this commission has required hospitals to create credentialing boards to evaluate physician ability.
Clinics and hospitals use a similar procedure to obtain and validate information from various sources during credentialing. Documentation requirements are the same whether a physician is new or transferring from another medical entity.
Staff initiate requests and verify essential documentation using sources. After completion, the credentialing team submits insurance applications. This complicated process ensures healthcare providers follow hospital standards
This Documentation Includes
- State license.
- Board qualification.
- Certification status.
- Driver’s license.
- Social Security card.
- Surgical logs.
- Documents of hospital privileges.
- 3 letters of recommendation.
- Updated curriculum vitae.
- ACLS/BLS certification.
- DEA certificate.
- Mammo #s and MQSA (if applicable).
- Current CME (CME activity for the past three years).
- Residency diploma.
- Military discharge record -Form DD-214 (if applicable).
- Current immunization records and most recent TB test results (if available).
- Copy of NBME, FLEX, USMLE, or SPEX scores.
- Copy of BLS, ACLS, ATLS, PALS, APLS, and NRP certificate(s).
- For foreign graduates, ECFMG certificate number.
- Immunization records.
- School diploma.
- Professional reference(s).
- Residency diploma.
Hospitals might maintain high standards and reduce risks by authenticating the credentials and capability of healthcare providers.
After completing the application review, the hospital governing board will consider the application for approval. Sometimes applicants may be requested to undergo an additional, comprehensive evaluation before receiving their final decision.
Why is Credentialing Important?
Before discussing the steps, let’s answer why credentialing is essential in healthcare. Credentialing contributes to quality assurance in healthcare. By evaluating the qualifications and track records of healthcare providers, hospitals can maintain high standards of care. This process helps identify practitioners who have demonstrated excellence in their field, promoting a culture of quality and enhancing patient outcomes.
Although credentialing for hospitals are crucial for regulatory compliance, healthcare organizations must adhere to various regulatory requirements and accreditation standards.
By verifying the credentials of medical staff members, hospitals ensure compliance with these rules & regulations, protecting both patients and the organization itself from legal and financial consequences. Read for more information.
Most hospitals and healthcare practices must ensure their providers have the proper credentials to process insurance claims. Ensuring patients receive quality care from providers who have fulfilled state licensure and certification requirements.
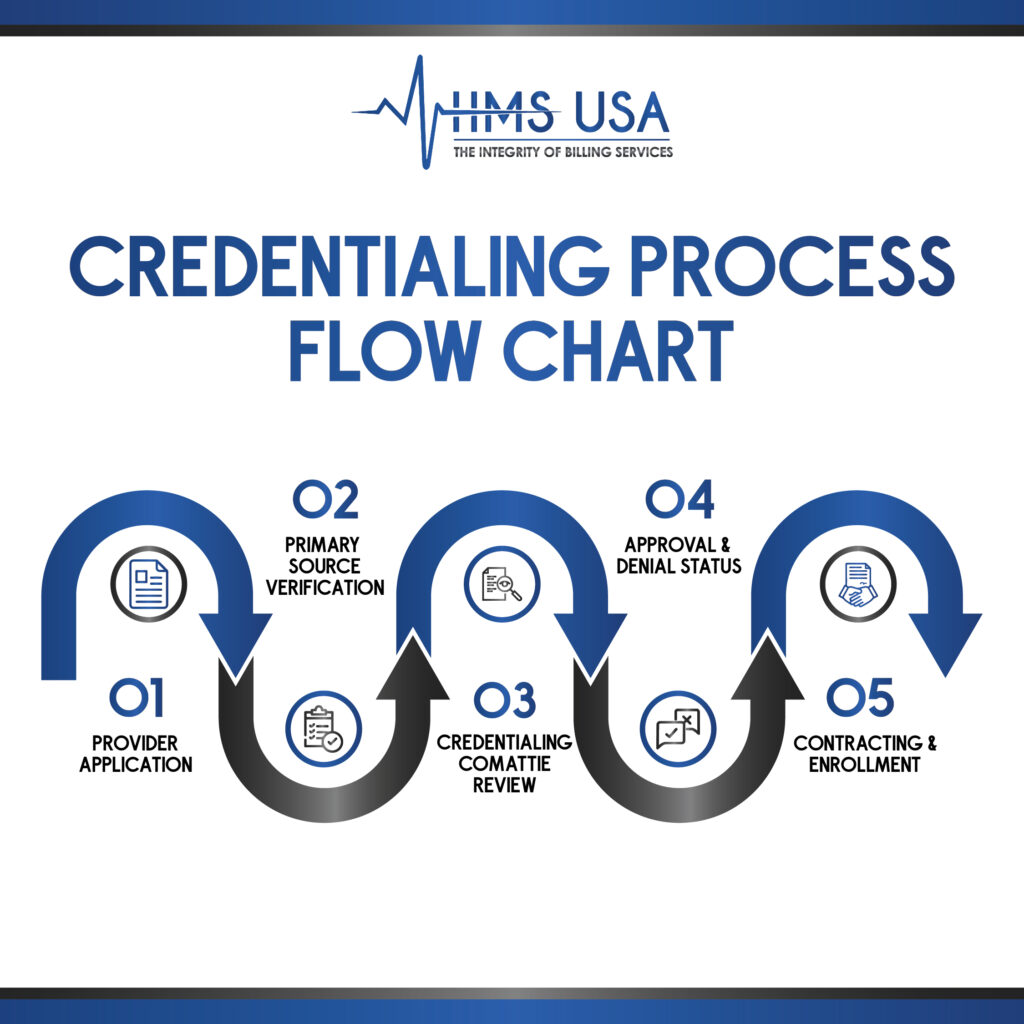
Application Submission
Each healthcare organization has its application. The hospital credentialing process begins with healthcare physicians submitting an application to the hospital or healthcare organization.
The application typically includes all essential information, personal and educational background, training history, work experience, licensure details, certifications, and references. In some exceptional cases, applications range from 10 to 100+ pages.
Primary Source Verification
Once the application is received, hospitals credentialing department initiates primary verification. This entails personally confirming its ligit source that the information provided in the application is accuracy.
Verification of primary sources may involve looking into credentials such as diplomas, training courses, licences, certificates, work experience, and malpractice records.
Credentials Committee Review
The third and important phase in hospital credentialing process for physicians is committee review the application, composed of healthcare professionals and administrators, reviews the application and necessary documents.
They assess the applicant’s malpractice carriers, work history, education, and peer references based on predefined criteria and standards. The committee may also conduct interviews
Verifications
Peer Review In addition to the credentials committee review, hospitals often conduct this reviews as part of the hospital credentialing process. Peers, such as other physicians or healthcare providers within the hospital, evaluate the applicant’s clinical skills, professionalism, and ability to work.
Decision - Making and Approval
Based on the findings from the credentials committee and peer review, a decision is made regarding the applicant’s eligibility for medical staff membership and privileges. If approved, the hospital grants specific privileges based on the healthcare professional’s qualifications and expertise.
Generally, heads of department and hospital boards meet to finalize the application and documents and make decision for physician’s appointment.
In another scenario some facilities require approval from medical staff services office’s only. Depends on the meetings, how long this process will take time.
Monitoring and Reappointment
Credentialing is not a one-time process, it requires ongoing monitoring to ensure that it meet the specific standards. Hospitals have credentialing processes that typically take place every two years or as per regulatory requirements. This includes reviewing the practitioner’s performance, continuing education, licensure status, and any changes in their practice.
Phases For Hospital Provider Credentialing
The three primary stages of healthcare provider credentialing:
1. Information Gathering
A healthcare facility may asks the provider for information about education, practice background, licenses, etc. Provider response through email or software about asked information.
The healthcare facility or insurance plans works with a third party named as credentials verification organization.
2. Check The Information
The facility or insurance company will conduct an examination to confirm the provider’s information, they will speak with licencing bodies, medical institutions, and other organizations directly.
In other condition, with the help of credentialing software to check information that licensing agencies make available online.
Many healthcare organizations use work management platforms to help them generate and maintain record provider information, which get automatic updates when any credentialing application get expired or re-checked if required.
It includes monitoring about medical incidents, practice claims, or other information that could raise questions about provider credential or re-credential.
3. Award The Provider With Credentials
When an organization verifies credentials and found no issues, the healthcare facility mark credentials status enable for provider. When insurance company completes process, then it can decide to approve the provider.
That is, the insurance company only pay for those providers only for treating patients, who already insuranced with them.
Read More: Physician’s Billing Services: Some Advantages And Disadvantages 2023
Conclusion
Hospital credentialing ensures patient safety and maintains high healthcare standards for institutions and practitioners. Hospitals guarantee healthcare providers meet high standards by thoroughly confirming and reviewing qualifications.
The careful execution of hospital credentialing systems builds patient trust. Demonstrating the skills and qualifications of healthcare providers builds confidence and competence in healthcare facilities.






